Diabetes Complications Education
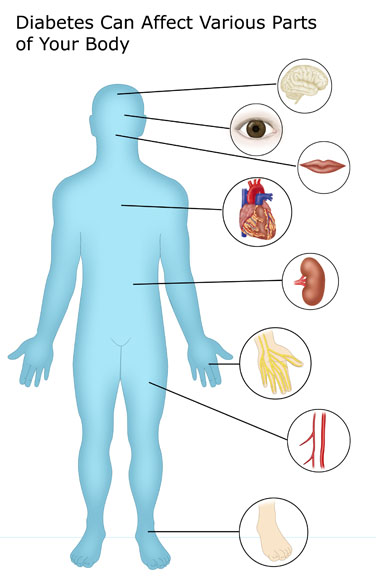
Long-term complications of diabetes develop gradually. the longer you have diabetes — and the less controlled your blood sugar — the higher the risk of complications. eventually, diabetes complications may be disabling or even life-threatening. possible complications include: cardiovascular disease. Diabetes and you: all medicines matter! pdf icon; what you need to know about diabetes and adult vaccines pdf icon; diabetes and you: healthy eyes matter! pdf icon [pdf 543k] diabetes and you: healthy feet matter! pdf icon [pdf 460k] diabetes and you: healthy teeth matter! pdf icon [pdf 669k] diabetes and hepatitis b vaccination pdf icon. Continued protect your feet. type 1 diabetes can take a toll on your feet. nerve damage can make them numb or tingly, and it can weaken or destroy the tissue in them. infections and ulcers are. Diabetes is the leading cause of new vision loss among adults ages 20 to 74 in the u. s. it can lead to eye problems, some of which diabetes complications education can cause blindness if not treated: glaucoma.
Diabetes self-management education and support (dsmes) services help people with diabetes learn how to take the best care of themselves. ask your doctor for a referral to dsmes services to help you manage your diabetes. Managing your diabetes will help you avoid or delay serious health complications. the skills you learn will help you take better care of yourself. diabetes management starts with you. it’s important to go for dsmes services when you first find out you have diabetes so you can learn how to take care of yourself.
Diabetes Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic
Diabetes education online. the long-term risk of developing complications from diabetes can be decreased through blood glucose and blood pressure control. Complications. type 2 diabetes can be easy to ignore, especially in the early stages when you're feeling fine. but diabetes affects many major organs, including your heart, blood vessels, nerves, eyes and kidneys. controlling your blood sugar levels can help prevent these complications. Diabetescomplications often share the same risk factors, and one complication can make other complications worse. for example, many people with diabetes also have high blood pressure, which in turn worsens eye and kidney diseases. diabetes tends to lower hdl (“good”) cholesterol and raise triglycerides (a kind of blood fat) and ldl (“bad. Intensive blood glucose control is the best way to avoid diabetic complications. high blood glucose levels do not always cause symptoms, and can silently cause damage to the cells. this is why diabetes is called the silent killer.
Skin complications. stay alert for symptoms of skin infections and other skin disorders common in people with diabetes. read more. eye complications. keep your risk of glaucoma, cataracts and other eye problems low with regular checkups. read more. neuropathy. nerve damage from diabetes is called diabetic neuropathy (new-rop-uh-thee). Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the cdc website.. the centers for disease control and prevention (cdc) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website. linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an diabetes complications education endorsement by cdc or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website. Diabetes care: 10 ways to avoid diabetes complications (mayo foundation for medical education and research) also in spanish; diabetes, gum disease, and other dental problems (national institute of diabetes and digestive and kidney diseases) also in spanish; understanding blood sugar and control (american diabetes association); weight loss (american diabetes association).
Foot complications. people with diabetes can develop many different foot problems. even ordinary problems can get worse and lead to serious complications. foot problems most often happen when there is nerve damage, also called neuropathy. this can cause tingling, pain (burning or stinging), or weakness in the foot. Eye complications with diabetes. diabetes is the leading cause of new blindness in adults ages 20 to 74. patients with diabetes are 25 times more likely to become legally blind than are patients without diabetes. there are three eye-related major complications: retinopathy, cataracts, and glaucoma. Diabetes self management patient education materials. table of contents. click on any of the links below to access helpful materials on managing all aspects of diabetes that can be printed and given to your patients. nine ways to avoid diabetes complications:. Introducing pietro marsala @marsala90, diabetes warrior, and now, eligible commercial pilot. read more about how the ada advocated for this change, here (link in story): bit. ly/2rnfdab or visit diabetes. org for more connectedforlife.
Cardiovascular disease: affects the heart and blood vessels and may cause fatal complications such as coronary artery disease (leading to heart attack) and stroke. cardiovascular disease is the most common cause of death in people with diabetes. high blood pressure, high cholesterol, high blood glucose and other risk factors contribute to increasing the risk of cardiovascular complications. Children who are exposed for a long time to high blood glucose in the womb are at higher risk of developing diabetes in the future. learn more about diabetes in pregnancy. oral complications: people with diabetes have an increased risk of inflammation of the gums (periodontitis) if blood glucose is not properly managed. periodontitis is a major cause of tooth loss and is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (cvd). Eventually, diabetes complications may be disabling or even life-threatening. possible complications include: cardiovascular disease. diabetes dramatically increases the risk of various cardiovascular problems, including coronary artery disease with chest pain (angina), heart attack, stroke and narrowing of arteries (atherosclerosis). Uncontrolled diabetes can cause serious complications. these complications can potentially lower your quality of life, raise your risk of disability, and increase your chances of early death.
Complications of diabetes • diabetes is a chronic (or lifelong) disease that can result in both long term and short term complications. • long term complications are caused by years of high blood sugar levels in the blood vessels. • risk of complications increase the longer blood sugar levels are not under control. See more videos for diabetes complications education. Nerve damage (neuropathy): one of the most common diabetes complications, nerve damage can cause numbness and pain. nerve damage most often affects the feet and legs but can also affect your digestion, blood vessels, and heart.
International Diabetes Federation Complications

Although long-term complications of diabetes develop gradually, they can eventually be disabling or even life-threatening. some of the potential complications of diabetes include: heart and blood vessel disease. diabetes dramatically increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, high blood pressure and narrowing of blood vessels (atherosclerosis). Diabetes makes it more likely you'll get certain illnesses. routine vaccines can help prevent them. ask your doctor about: flu vaccine. a yearly flu vaccine can help diabetes complications education you stay healthy during flu season as well as prevent serious complications from the flu.
People with diabetes are more likely to have gum disease, which can lead to tooth loss. gum disease can also make blood sugar levels rise and make diabetes harder to manage. treating gum disease can lower blood sugar over time and reduce the chance of other diabetes problems, such as heart disease and kidney failure. New diabetes cases have decreased over the last decade except in people younger than 20 years. and in adults, there is much room for improvement in preventing diabetes complications. data from this report can help focus critical type 2 diabetes prevention and diabetes management efforts across the nation.
Comments
Post a Comment