Diabetes Complications Review Article
Glucose by target cells. diabetes mellitus is aggravated by and associated with metabolic complications that can subsequently lead to premature death. this review explores diabetes mellitus in terms of its historical perspective, biochemical basis, economic burden, management interventions along with the future perspectives. The prevalence of diabetes (dm) is constantly increasing worldwide at an alarming rate. according to the international diabetes federation in 2015, an estimated 415 million people globally were suffering from this condition []. complications of dm account for increased morbidity, disability, and mortality and represent a threat for the economies of all countries, especially the developing ones []. Diabetes is a disease chronic disease which affects global population from long time. this review is an update on unknown complications, diabetes complications review article causes, treatment modalities of this disease. this article also provides a summary on disease management through various strategies. keywords. diabetes, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic complications. introduction. Journal of diabetes and its complications (jdc) is a journal for health care practitioners and researchers, that publishes original research about the pathogenesis, diagnosis and management of diabetes mellitus and its complications. jdc also publishes articles on physiological and molecular aspects of glucose homeostasis.
Complications Of Diabetes 2017 Hindawi
The present special issue includes articles on macrovascular complications of dm as well. j. zhang et al. in the article entitled “coronary plaque characteristics assessed by 256-slice coronary ct angiography and association with high-sensitivity c-reactive protein in symptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes” have performed a coronary. Background type 2 diabetes mellitus (t2dm) is a global epidemic associated with increased health expenditure, and low quality of life. many non-genetic risk factors have been suggested, but their overall epidemiological credibility has not been assessed. methods we searched pubmed to capture all meta-analyses and mendelian randomization studies for risk factors of t2dm. Diabetes complications include possible blindness, amputation of lower limb, renal failure, and cardiac arrest or stroke. this review summarizes the pathophysiology for both types of dm, the. Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic disorders with high mortality and morbidity associated with complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, and stroke. the prevalence of diabetes is 9. 4% in us adults, and prevalence increases markedly with age, with 1 in 4 adults aged ≥65 years affected by diabetes.

A systematic review (78 studies from 84 cohorts) reports a prevalence of 0. 003-2. 8% for diabetes related peripheral neuropathy and 0. 01-0. 4% for diabetes related peripheral arterial disease. 4 figure 1 ⇓ depicts factors that contribute to foot complications. The global increase in type 2 diabetes prevalence is well documented, but international trends in complications of type 2 diabetes are less clear. the available data suggest large reductions in classic complications of type 2 diabetes in high-income countries over the past 20 years, predominantly reductions in myocardial infarction, stroke, amputations, and mortality. A review on diabetes diabetes complications review article mellitus: complications, management and treatment modalities dattatreya adapa 1 and sarangi tk 2 *. 1 gitam institute of sciences, gitam university, visakhapatnam, andhrapradesh, india. 2 school of biosciences and technology, vit university, vellore, tamil nadu, india *corresponding author: sarangi tk school of biosciences and technology.
Pdf Gestational Diabetes And Its Maternal And Neonatal

Omics International Open Access Journals Scientific Conferences And Events Organizer
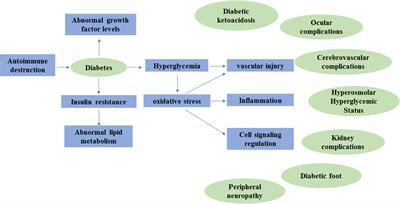
Diabetes complications are common among patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes but, at the same time, are responsible for significant morbidity and mortality. the chronic complications of diabetes are broadly divided into microvascular and macrovascular, with the former having much higher prevalence than the latter [ 2 ]. Definition and description. type 1 diabetes (t1d) is a t-cell mediated autoimmune disease in which destruction of pancreatic β-cells causes insulin deficiency which leads to hyperglycemia and a tendency to ketoacidosis. 1 excesses glucose levels must be managed by exogenous insulin injections several times a day. 2 patients with t1d constitute 5-10% of all people with diabetes, the remainder. In this review, we synthesise data from adult population-based studies on trends in diabetes complications based on original articles, review articles and meta-analyses, with the objectives of: (1) characterising recent and long-term trends in diabetes-related complications; (2) describing regional variation in the excess risk of complications. Diabetescomplications are common among patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes but, at the same time, are responsible for significant morbidity and mortality. “socioeconomic inequalities in mortality, morbidity and diabetes management for adults with type 1 diabetes: a systematic review,” plos one, vol. 12, no. 5, article e0177210, 2017.
Background diabetes complications review article type 2 diabetes mellitus (t2dm) is a global epidemic associated with increased health expenditure, and low quality of life. many non-genetic risk factors have been suggested, but their overall epidemiological credibility has not been assessed. methods we searched pubmed to capture all meta-analyses and mendelian randomization studies for risk factors of t2dm. for each association. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (t2dm) is an expanding global health problem, closely linked to the epidemic of obesity. individuals with t2dm are at high risk for both microvascular complications. Title:prevention of vascular complications in diabetes mellitus patients: focus on the arterial wall volume: 17 issue: 1 author(s):mojca lunder, miodrag janić and mišo Šabovič* affiliation:department of vascular diseases, university medical centre ljubljana, zaloska cesta 7; si-1000 ljubljana, department of vascular diseases, university medical centre ljubljana, zaloska cesta 7; si-1000.
Type 1 Diabetes A Clinical Perspective
According to the research objective, this study is a review article and an applied research in terms of methodology which tries to identify and treat gestational diabetes and its complications on.
Socioeconomic inequalities and type 2 diabetes.
This review offers a discussion of various strategies for the prevention of type 2 diabetes. it includes results from recent clinical trials targeting patients who are at highest risk for the development of diabetes, with a particular emphasis on lifestyle modification strategies and the implementation of such programs in community-based settings. Chronic complications of diabetes mellitus: a mini review article (pdf available) in current diabetes reviews 13(1) · october 2015 with 9,027 reads how we measure 'reads'. Over a recent period of 10 years, 28 studies were published on the impact of ses on diabetes complications in high-income countries. from their data, our present review has established a socioeconomic gradient for all types of diabetes complications, but especially retinopathy and cardiopathy, the most well-documented of complications. Diabetescomplications include possible blindness, amputation of lower limb, renal failure, and cardiac arrest or stroke. this review summarizes the pathophysiology for diabetes complications review article both types of dm, the.
the physiology and pathophysiology of diabetes and its complications in diabetes care and treatment, as well as mini-reviews of landmark studies, practical treatment pointers, and best Diabetes is disproportionately increasing in lowand middle-income countries due partly to rapid urbanization, lifestyle changes, and limited resources. this is the first comprehensive review of prevalence, risk factors, complications and costs related to diabetes in ethiopia. us reprints and permissions omics international white paper review articles press releases open access scientific reports new initiatives my personal experience, most of our original medical articles would be published within 3 weeks moreover, the editorial boards of most the omics international journals have many dedicated and reputed scientists as editorial members thus, i am grateful for their assistance and currently review work of other scientists da-yong lu doctor In this research topic, we welcome original research articles (including meta-analyses) or reviews on clinical research, basic human studies, and animal studies, which deal with topics related to diabetes and its complications but with focuses on endothelial dysfunction -pathogenesis, etiology, epidemiology, assessment, prevention, and treatment.
Comments
Post a Comment