Diabetes Complications Macrovascular And Microvascular

Recommendations. 11. 2 optimize glucose control to reduce the risk or slow the progression of chronic kidney disease. a. 11. 3 for patients with type 2 diabetes and diabetic kidney disease, consider use of a sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor in patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate ≥30 ml/min/1. 73 m 2 and urinary albumin >30 mg/g creatinine, particularly in those with. Relationship between hba1c and risk of micro/macrovascular complications and healthcare costs among type 2 diabetes poor glycemic control (>7. poor glycemic control (>7. 0%) in patients with type 2 diabetes (t2d) may increase risk of complications, leading to higher healthcare costs. Furthermore, saudi diabetes patients have lack of awareness about diabetes risk factors, which leads to the risk for microvascular complications. 4,5 from a recent study in saudi arabia, it became evident that around 40. 3% of patients with diabetes were unaware of dm. 71 another study reported that the diabetes knowledge score among the saudi.
Who About Diabetes
Diabetes is a leading cause of microvascular complications such as nephropathy and retinopathy. it is also associated with an accelerating atherosclerosis, and type 2 diabetes mellitus (t2dm) is usually not detected until late in the course of cardiovascular disease (cvd). Among macrovascular diabetes complications, coronary heart disease has been associated with diabetes in numerous studies beginning with the framingham study. 24 more recent studies have shown that the risk of myocardial infarction (mi) in people with diabetes is equivalent to the risk in nondiabetic patients with a history of previous mi. 25. One of the chief injuries arising from hyperglycemia is injury to vasculature, which is classified as either small vascular injury (microvascular disease) or injury to the large blood vessels of the body (macrovascular disease). Start studying macrovascular and microvascular complications in diabetes. learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Who About Diabetes
The relationship of glycemic exposure (hba1c) to the risk of development and progression of retinopathy in the diabetes complications macrovascular and microvascular diabetes control and complications trial. diabetes 1995; 44:968. reichard p, nilsson by, rosenqvist u. the effect of long-term intensified insulin treatment on the development of microvascular complications of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes is a disease that is strongly associated with both microvascular and macrovascular complications, including retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy (microvascular) and ischemic heart disease, peripheral vascular disease, and cerebrovascular disease (macrovascular), resulting in organ and tissue damage in approximately one third to one.
11 Microvascular Complications And Foot Care Standards

The body (macrovascular disease). as medical science advances increasingly toward prevention of complications of diabetes, it is important for clinicians to be familiar with the relationship between diabetes control and vascular injury. microvascular complications of. diabetes diabetic retinopathy. diabetic retinopathy may be the most. Definitions. microvascular complications of diabetes are those long-term complications that affect small blood vessels. these typically include retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy. retinopathy is divided into two main categories: nonproliferative retinopathy and proliferative retinopathy. ; nonproliferative retinopathy is the development of microaneurysms, venous loops, retinal hemorrhages. Macrovascularcomplications include cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks, strokes and insufficiency in blood flow to legs. there is evidence from large randomized-controlled trials that good metabolic control in both type 1 and 2 diabetes can delay the onset and progression of these complications. Microvascular complications of diabetes are those long-term complications that affect small blood vessels. these typically include retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy. retinopathy is divided diabetes complications macrovascular and microvascular into two main categories: nonproliferative retinopathy and proliferative retinopathy.
Microvascular And Macrovascular Complications Of Diabetes
The prevalence of type 2 diabetes is increasing in the united states and worldwide. because of many complications and the high costs of diabetes, its prevention and its complications demand more attention. the major complications of diabetes are cardiovascular diseases (cvd)—both microvascular disease and macrovascular disease. Diabetic retinopathy, nephropathy and neuropathy are the major microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus (t2dm) and their presence can accentuate the risk of cardiovascular disease. hyperglycemia, hypertension, genetic susceptibility among other risk factors play a significant role in the development and progression of these. There are two main types of complications of diabetes, which are called microvascular and macrovascular. macrovascular, referring to the term macro, involves issues with macro circulation, which is the circulatory system itself, in other words causing disease in the cardiovascular system itself, while the micro kind involves micro circulation, involving things such as the eyes, the kidneys.
11 Microvascular Complications And Foot Care Standards
Diabetesmacrovascularcomplications are diseases of the blood vessels caused in diabetes patients, influenced by factors like high cholesterol, insulin resistance, smoking, high blood sugar, high blood pressure and blood clotting disorders. there are three main macro vascular complications of diabetes that happen due to an increased risk of atherosclerosis.
Association between pre-diabetes and microvascular and.
Microvascular and macrovascular complications of diabetes.
The longer you have diabetes — and the less controlled your blood sugar — the higher the risk of complications. long-term complications of diabetes develop gradually. eventually, they may be disabling or even life-threatening. overall, diabetes complications can be studied into 2 majors i. e. microvascular and macrovascular. Pre-diabetes before diagnosis of type 2 diabetes is associated with increased odds of microvascular disease and acute coronary syndrome. detection of pre-diabetes might represent an opportunity for reducing the burden of microvascular and macrovascular disease through heightened attention to screening for vascular complications. Importantly, studies have shown that microvascular complications in the heart and brain precede the development of macrovascular complications in diabetic individuals. 10, 11 this review focuses on the different pathways and components that bring about the microvascular complications in diabetes mellitus and attempts to discuss the complex.
Diabetes complications are divided into microvascular (due to damage to small blood vessels) and macrovascular (due to damage to larger blood vessels). microvascular complications include damage to eyes (retinopathy) leading to blindness, to kidneys (nephropathy) leading to renal failure and to nerves (neuropathy) leading to impotence and diabetic foot disorders (which include severe infections leading to amputation). Complications of diabetes? diabetes-related complications can include damage to: » the large blood vessels (macrovascular/ cardiovascular complications), leading to heart attack, stroke or circulation problems in the lower diabetes complications macrovascular and microvascular limbs » the small blood vessels (microvascular complications), causing problems in the eyes, kidneys, feet and nerves. Generally, the injurious effects of hyperglycemia are separated into macrovascular complications (coronary artery disease, peripheral arterial disease, and stroke) and microvascular complications (diabetic nephropathy, neuropathy, and retinopathy).
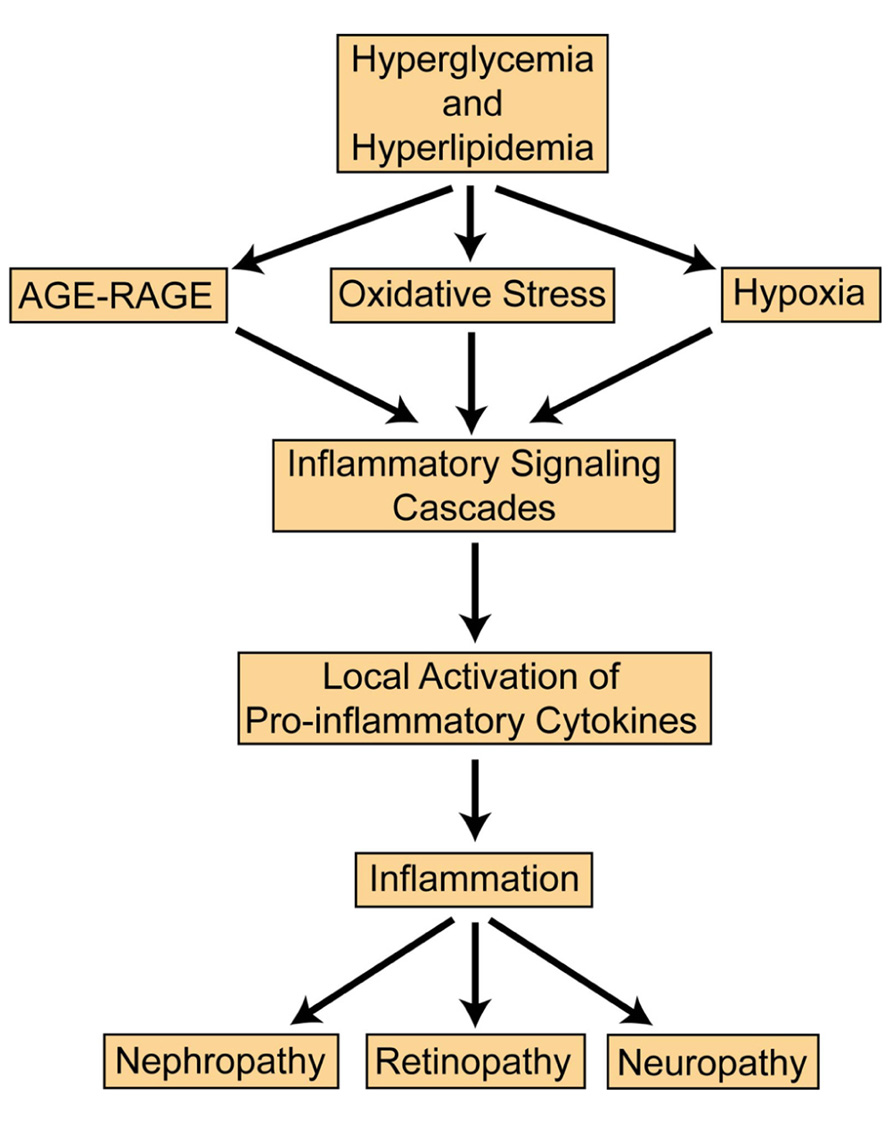
The chronic complications are mainly the result of longstanding damage to blood vessels. these complications are grouped as microvascular due to basement membrane thickening or macrovascular due to. 11. microvascular complications and foot care: insulin alone was used to lower blood glucose in the diabetes control and complications trial (dcct)/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications (edic) study of type 1 diabetes, while a variety of agents were used in clinical trials of type 2 diabetes, supporting the conclusion. Eventually, they may be disabling or even life-threatening. overall, diabetes complications can be studied into 2 majors i. e. microvascular and macrovascular. this write-up highlighting the microvascular complications of diabetes. microvascular complications. damage to small blood vessels is called microangiopathy or microvascular disease.
Diabetes mellitus can lead to many acute and chronic complications. the chronic complications are mainly the result of longstanding damage to blood vessels. these complications are grouped as microvascular due to basement membrane thickening or macrovascular due to accelerated atherosclerosis. More diabetes complications macrovascular and microvascular images. Risk of macrovascular dc increased 2% and risk of microvascular dc 3% for each one unit increase in hba1c (hazard ratio=1. 02, 95% ci 1. 01-1. 03 and 1. 03, 95% ci 1. 02-1. 04, respectively). among the 11,053 patients with 2+ years follow-up, total mean adjusted diabetes complications macrovascular and microvascular costs were $26,167 (95% ci $25,929-$26,406) and did not differ by hba1c strata.
Comments
Post a Comment