Diabetes Complications Review
10 known diabetes complications webmd.

Journal of diabetes and its complications (jdc) is a journal for health care practitioners and researchers, that publishes original research about the pathogenesis, diagnosis and management of diabetes mellitus and its complications. jdc also publishes articles on physiological and molecular aspects of glucose homeostasis. Macrovascular complications of diabetes, including coronary heart disease, stroke and peripheral vascular disease, and microvascular complications, such as end-stage renal disease (esrd), retinopathy and neuropathy, along with lower-extremity amputations (lea), are responsible for much of the burden associated with diabetes. Type 2 diabetes can increase your risk of a number of complications that affect the feet. most diabetes-related foot issues are caused by nerve damage, sometimes referred to as neuropathy. This free course, diabetes complications, looks at the way the condition is managed once it has been diagnosed in order to reduce the risk of further complications. you will look at the role of each member of the team involved in the diabetes annual review and look at the risk factors involved with certain diabetes complications.
These complications occur in the majority ofindividuals with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. among the most prevalentmicrovascular complications are kidney disease, blindness, and amputations, with current therapies only slowing disease progression. Skin complications. stay alert for symptoms of skin infections and other skin disorders common in people with diabetes. read more. eye complications. keep your risk of glaucoma, cataracts and other eye problems low with regular checkups. read more. neuropathy. nerve damage from diabetes is called diabetic neuropathy (new-rop-uh-thee). Diabetes is the leading cause of new vision loss among adults ages 20 to 74 in the u. s. it can lead to eye diabetes complications review problems, some of which can cause blindness if not treated: glaucoma. type 2 diabetes mellitus cochrane database of systematic reviews 2005;(3):cd002966 39 uk prospective diabetes study group effect of intensive blood glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (ukpds type 2 diabetes mellitus cochrane database of systematic reviews 2003;(2):cd002967 41 uk prospective diabetes study(ukpds) group intensive blood glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (ukpds 33)
The global increase in type 2 diabetes prevalence is well documented, but international trends in complications of type 2 diabetes are less clear. the available data suggest large reductions in classic complications of type 2 diabetes in high-income countries over the past 20 years, predominantly reductions in myocardial infarction, stroke, amputations, and mortality. Diabetes is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) that results from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both, and affects multiple systems of. See more videos for diabetes complications review.

Understanding some common complications of diabetes can help you recognize the early warning signs and take action to prevent more serious problems. learn more from the experts at webmd. 1. physiol rev. 2013 jan;93(1):137-88. doi: 10. 1152/physrev. 00045. 2011. mechanisms of diabetic complications. diabetes complications review forbes jm(1), cooper me. author information: (1)diabetes division, baker idi heart and diabetes institute, melbourne, australia. it is increasingly apparent that not only is a cure for the current worldwide diabetes epidemic required, but also for its major complications, affecting.
Mechanisms Of Diabetic Complications Physiological Reviews

25-09:50 专题报告 symposium 糖尿病及其并发症的预防 prevention of diabetes and its complication shaw watanabe 亚太临床营养学会 asia pacific clinical nutrition society 1 13:30-14:00 专题报告 symposium 益生菌益生元与糖尿病证据体综述 review on probiotics and diabetes 刘烈刚 liegang liu 华中科技大学公共卫生学院 school of public health, If left untreated, dm can lead to a number of diseases and long-term complications leading subsequently to death. areas covered: in this mini review, we aim to highlight a number of complications, cascades or pathways (polyol, hexosamine, protein kinase c, advanced glycation-end product) of events and cellular, sub-cellular and molecular mechanisms associated with dm-induced hyperglycaemia (hg). regional in 2017 after passing out because of complications from type 1 diabetes the hospital had given her medication to stabilize
Areas covered: in this mini review, we aim to highlight a number of complications, cascades or pathways (polyol, hexosamine, protein kinase c, advanced glycation-end product) of events and cellular, sub-cellular and molecular mechanisms associated with dm-induced hyperglycaemia (hg). Diabetes is the sixth leading cause of death in the u. s. and is associated with increased risk for heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, blindness, and amputations [4,5]. 1. 3 the diabetes annual review. the function of the diabetes annual review is to identify risk factors. the gp or diabetes complications review a doctor in the hospital diabetes team may perform this review, while other members of the team, for example the practice nurse in the gp surgery, or the diabetes care technician in the diabetes clinic, carry out many of the tests. A review on diabetes mellitus: complications, management and treatment modalities dattatreya adapa 1 and sarangi tk 2 *. 1 gitam institute of sciences, gitam university, visakhapatnam, andhrapradesh, india. 2 school of biosciences and technology, vit university, vellore, tamil nadu, india *corresponding author: sarangi tk school of biosciences and technology.
In this review, we synthesise data from population-based studies on trends in diabetes complications, with the objectives of: (1) characterising recent and long-term trends in diabetes-related complications; (2) describing regional variation in the excess risk of complications, where possible; and (3) identifying and prioritising gaps for. diet ? categories alcohol (21) bariatric surgery (3) book reviews (35) cancer (23) carbohydrate (101) causes of diabetes (55) coronary heart disease (59) dairy products (8) dementia (22) diabetes complications (50) dm prevalence (8) drugs for diabetes (96)
Diabetes & its complications (issn 2639-9326) is a global peer-reviewed open access journal that emphasis on the different aspects of clinical diabetes, the broad scope will also include significant research in the fields of pathology and therapeutic innovations of diabetes itself, both type i and ii. If it is not controlled, diabetes can cause a host of complications that can affect nearly every organ in the body. diabetes complications include: heart disease; stroke; kidney disease; nerve. Diabetes is the leading cause of new vision loss among adults ages 20 to 74 in the u. s. it can lead to eye problems, some of which can cause blindness if not treated: glaucoma; cataracts.
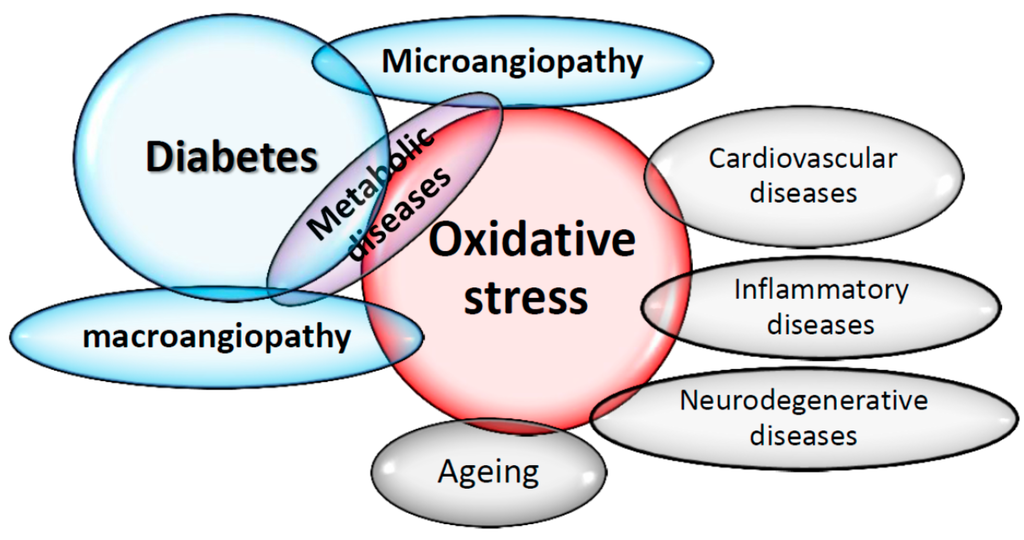
Glucose by target cells. diabetes mellitus is aggravated by and associated with metabolic complications that can subsequently lead to premature death. this review explores diabetes mellitus in terms of its historical perspective, biochemical basis, economic burden, management interventions along with the future perspectives. This review will focus on arguably the most devastating consequence of diabetes, its long-term vascular complications. these complications are wide ranging and are due at least in part to chronic elevation of blood glucose levels, which leads to damage of blood vessels (angiopathy; figure 1 ). the physiology and pathophysiology of diabetes and its complications in diabetes care and treatment, as well as mini-reviews of landmark studies, practical treatment pointers, and best Diabetes complications often share the same risk factors, and one complication can make other complications worse. for example, many people with diabetes also have high blood pressure, which in turn worsens eye and kidney diseases. diabetes tends to lower hdl (“good”) cholesterol and raise triglycerides (a kind of blood fat) and ldl (“bad”) cholesterol. these changes can increase the risk for heart disease and stroke.
A review on diabetes mellitus: complications, management.
Comments
Post a Comment