Diabetes Care Model
Team care approach for diabetes management a team approach to diabetes care can effectively help people cope with the vast array of complications that can arise from diabetes. people with diabetes can lower their risk group, and the advantages that can result from this model. diabetes healthsense: resources for living well. See more videos for diabetes care model.
Diabetes Basics Cdc

Successful diabetes care requires a patient’s consistent self-care behaviors such as attention diabetes care model to diet, exercise, preventive care measures, drug adherence, and self-monitored blood glucose. The american association for diabetes educator’s (aade’s) aade7 self-care behaviors ® (aade7) framework provides an evidence-based model for assessment, intervention, and evaluation of individuals and populations living with diabetes and other cardiometabolic conditions. 1 using the aade7 framework, diabetes care and education specialists partner with people living with diabetes and.
A patient-centered interdisciplinary diabetes care model was implemented at vidant medical center in greenville, n. c. a 909-bed tertiary care teaching hospital, for the purpose of providing all patients with diabetes clear and concise instructions on diabetes survival skills. The aade7 self-care behaviors provides a practical model that informs decision making among individuals living with diabetes and related conditions and the members of their healthcare team in their shared drive for improved health and quality of life. Diabetes is a prevalent condition. just recall all the patients you saw today and there’s probably a handful of them who diabetes care model are diabetic. according to the national center for chronic disease prevention and health promotion division of diabetes translation, up to 34. 2 million people in the united states have diabetes. and by 2049, the number can increase up to 700 million.
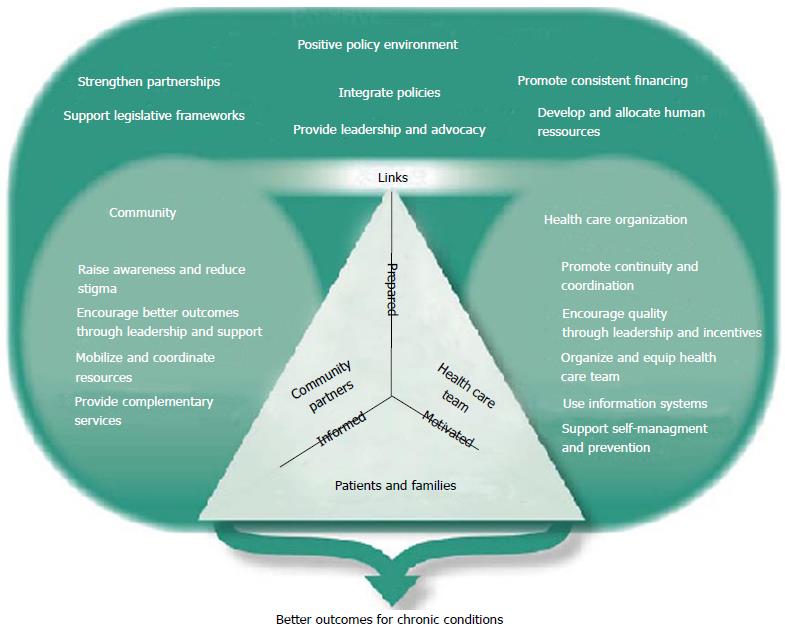
The chronic care model (ccm) uses a systematic approach to restructuring medical care to create partnerships between health systems and communities. the objective of this study was to describe how researchers have applied ccm in us primary care settings to provide care for people who have diabetes and to describe outcomes of ccm implementation. A team approach to diabetes care can effectively help people cope with the vast array of complications that can arise from diabetes. people with diabetes can lower their risk for microvascular complications, such as eye disease and kidney disease; macrovascular. The diabetes model of care provides a framework for comprehensive, accessible and efficient provision of coordinated diabetes prevention and management services for all western australians.
The Chronic Care Model For Type 2 Diabetes A Systematic
More diabetes care model images. The chronic care model (ccm) uses a systematic approach to restructure health care systems. the aim of this systematic review was to examine studies that evaluated different elements of diabetes care model the ccm in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (t2dm) and to assess the influence of the ccm on different clinical outcomes. there view was performed in the medline and cochrane library electronic databases. Evidence-based interventions can promote early diagnosis of diabetes, prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes, and improve treatment and outcomes for people with diabetes. diabetes & prediabetes tests; game plan for preventing type 2 diabetes; diabetes school guide; guiding principles for the care of people with or at risk for diabetes.
Aade7 self-care behaviorsthe framework for optimal self.
Successful diabetes care requires a systematic approach to supporting patients’ behavior change efforts, including 1) healthy lifestyle changes (physical activity, healthy eating, tobacco cessation, weight management, and effective coping), 2) disease self-management (taking and managing medication and, when clinically appropriate, self-monitoring of glucose and blood pressure), and 3) prevention of diabetes complications (self-monitoring of foot health; active participation in screening. Diabetes care *use the print, email and pdf buttons, to the right, to share only this page. to share the full product catalog, please use the product catalog > download option from the navigation bar at the top of the page. Diabetessymptoms vary depending on how much your blood sugar is elevated. some people, especially those with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes, may not experience symptoms initially. in type 1 diabetes, symptoms tend to come on quickly and be more severe. standards of medical care in diabetes — 2018. diabetes care. 2018;41:s1.
Diabetes is a chronic (long-lasting) disease that affects how your body turns food into energy. there are three main types of diabetes: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes (diabetes while pregnant). more than 122 million americans are living with diabetes (34. 2 million) or prediabetes (88 million). Chronic care model. although numerous interventions to improve adherence to the recommended standards have been implemented, a major barrier to optimal care is a delivery system that too often is fragmented, lacks clinical information capabilities, duplicates services, and is poorly designed for the coordinated delivery of chronic care. The chronic care model for type 2 diabetes: a systematic review abstract. the chronic care model (ccm) uses a systematic approach to restructure health care systems. the aim of this background. diabetes mellitus is currently a major chronic disease that affects individuals from countries at all. 2. proposed national model of integrated care for type 2 diabetes the national clinical programme for diabetes proposes to change how we deliver diabetes care to people with type 2 diabetes and support a national model of integrated care. the integrated care will be developed with the joint involvement of primary, secondary and tertiary sectors.
The chronic care model (ccm) was developed to provide chronic disease patients, including those with type 2 diabetes mellitus (t2dm), with forms of self-care and tracking systems. the model represents a method for restructuring health care through interactions between health systems and communities [5]. The american association for diabetes educator’s (aade’s) aade7 self-care behaviors ® (aade7) framework provides an evidence-based model for assessment, intervention, and evaluation of individuals and populations living with diabetes and other cardiometabolic conditions. 1 using the aade7 framework, diabetes care and education specialists partner with people living with diabetes and related conditions to support informed decision making. diabetes care and education specialists embrace a. Pediatric traumatic stress in primary care settings road map (6 to 18 years old) pediatric traumatic stress in child advocacy centers (cac) road map (6 to 18 years old) prescribing opioids for chronic non-cancer pain cpm.

Future diabetes care will continue to be delivered mainly in the primary care setting. efforts must continue to bridge the gap between evidence-based recommendations and the current outcomes of patients with diabetes. practice points improving care by delivering the chronic care model for diabetes management perspective. Professional practice committee: standards of medical care in diabetes—2020 2019 update to: management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. a consensus report by the american diabetes association (ada) and the european association for the study of diabetes (easd). The diabetes care model group at west ann arbor-parkland plaza how it works bi-weekly, a report is run in michart to find patients who have high a1c levels (hemoglobin that indicates whether or not a patient has diabetes), but whose most recent blood test is older than 90 days. The chronic care model (ccm) is a specific model aimed at switching care for patients with chronic diseases (e. g. type 2 diabetes, heart failure, stroke and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) from an acute and reactive intervention to a planned and proactive intervention, 5, 6 and at providing patients with self-management skills.
Comments
Post a Comment